SQL rollback section
Whenever we try to perform any statement in SQL it directly affects SQL rollback section. SQL statements such as Insert, Update or Delete when executed make a change in the relation. These changes has to be stored until the transaction lives; that is from begin to commit. When we say changes we mean the state of tuple before the particular operation was performed.
Why do we need rollbacks?
This is a way to maintain the atomicity property of databases. Either full transaction should be showed in effect or none. Hence, if for some reason - may it be hardware failure, power outages or software issue - a transaction fails the half-done effect of the transaction has to be reverted. This should bring back the database in the state before the transaction actually happened. These temporary changes, called as logs, reside in the SQL rollback section as per the SQL standards however, although the gist is same the actual implementation of SQL rollback defers from vendor to vendor. MySQL has Undo logs and Redo logs which work the magic to maintain the consistency and atomicity of the database.
“An undo log is a collection of undo log records associated with a single transaction. An undo log record contains information about how to undo the latest change by a transaction to a clustered index record. If another transaction needs to see the original data as part of a consistent read operation, the unmodified data is retrieved from undo log records. Undo logs exist within undo log segments, which are contained within rollback segments. Rollback segments reside in the system tablespace, undo tablespaces, and in the temporary tablespace.”
How does this operates?
InnoDB keeps a copy of everything that is changed
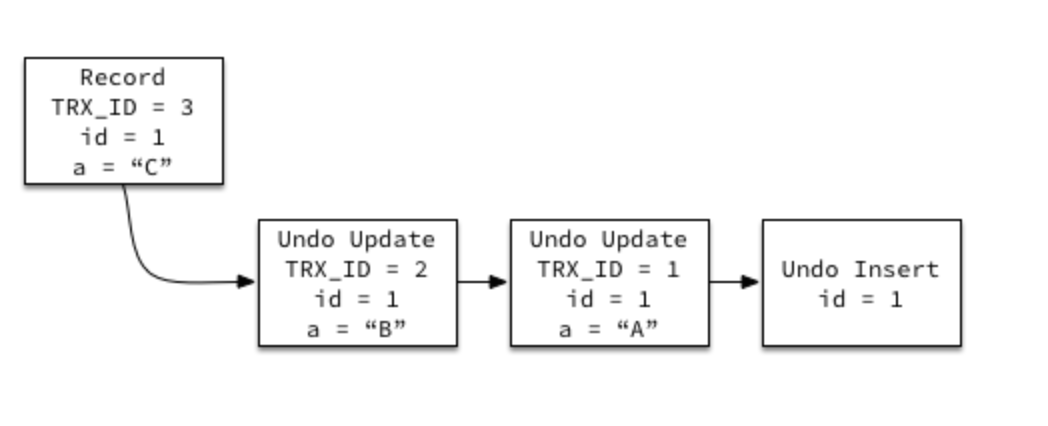
When a record is modified, the current (“old”) version of the data being modified is first stashed away as an “undo record” in an “undo log”. It’s called an undo log because it contains the information necessary to undo the change made by the user, reverting the record to its previous version.
Every record contains a reference to its most recent undo record, called a rollback pointer or ROLL_PTR, and every undo record contains a reference to its previous undo record (except for an initial record insert, which can be undone by simply deleting the record), forming a chain of all previous versions of a record.
In this way, any previous version of a record can be easily constructed, as long as the the undo records (the “history”) still exist in the undo logs.
Undo logs physical allocation
The undo log exists as pages allocated inside the InnoDB system tablespace (usually named ibdata1) and consumes its space there. What differentiates Undo log and Redo log is that Undo logs are built for rollback during the server is running while Redo log specialize on rollback during server crash. Such distinction of responsibility makes it possible for the Undo log to have a performance edge as it does not have to bother about crash perspective, and file based data-structure that the Redo log normally uses.
InnoDB supports a maximum of 128 rollback segments. We can use the following query to see the number of rollback segments.
sql SELECT @@innodb_rollback_segments;
The undo log pages are each part of a chain of undo log pages which form an undo segment, and consume a “slot” in a rollback segment. So, each rollback segment has a total of 1024 slots. We can show the max_undo_log size with the following query.
sql SELECT @@innodb_max_undo_log_size;
Note: We cannot set the innodb_max_undo_log_size < 10485760 [10 MB]
To change the number of segments and max undo log size:
sql SET GLOBAL innodb_max_undo_log_size = <>;sql SET GLOBAL innodb_rollback_segments = <>;
Default undo tablespaces are created in the location defined by the innodb_undo_directory variable. If the innodb_undo_directory variable is undefined, default undo tablespaces are created in the data directory. Default undo tablespace data files are named undo_001 and undo_002. The corresponding undo tablespace names defined in the data dictionary are innodb_undo_001 and innodb_undo_002.
“The initial size of an undo tablespace data file depends on the innodb_page_size value. For the default 16KB page size, the initial undo tablespace file size is 10MiB. For 4KB, 8KB, 32KB, and 64KB page sizes, the initial undo tablespace files sizes are 7MiB, 8MiB, 20MiB, and 40MiB, respectively.”